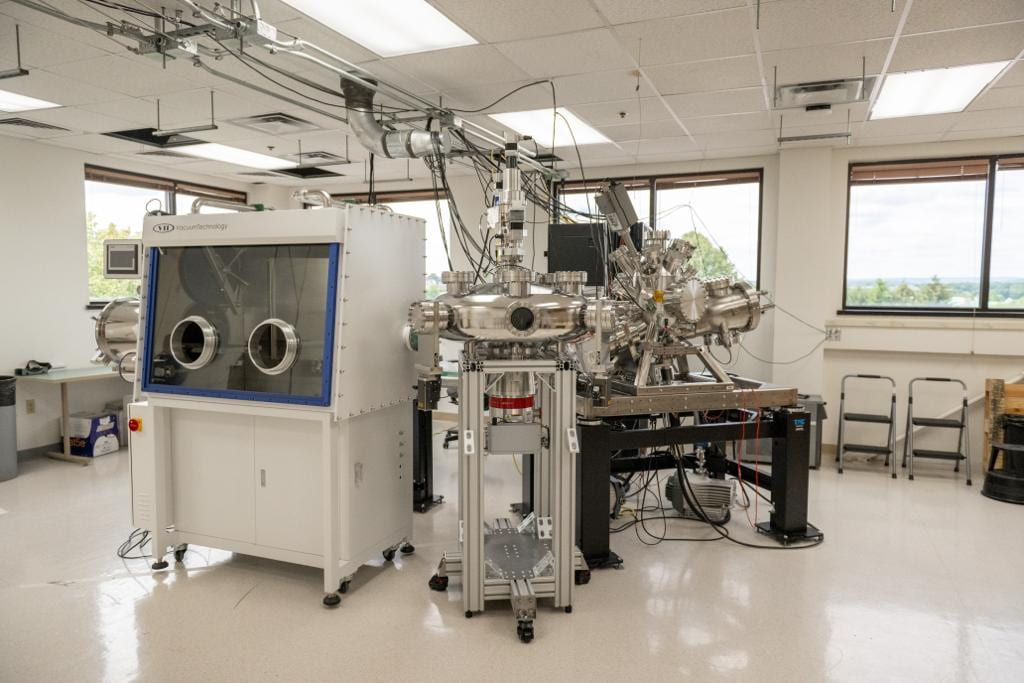
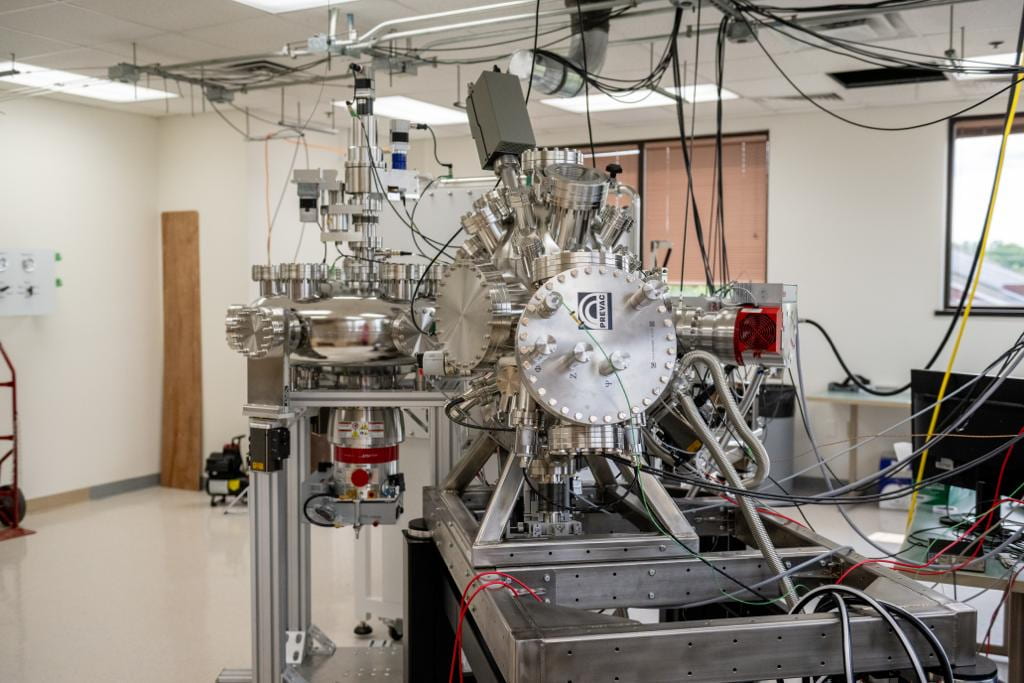
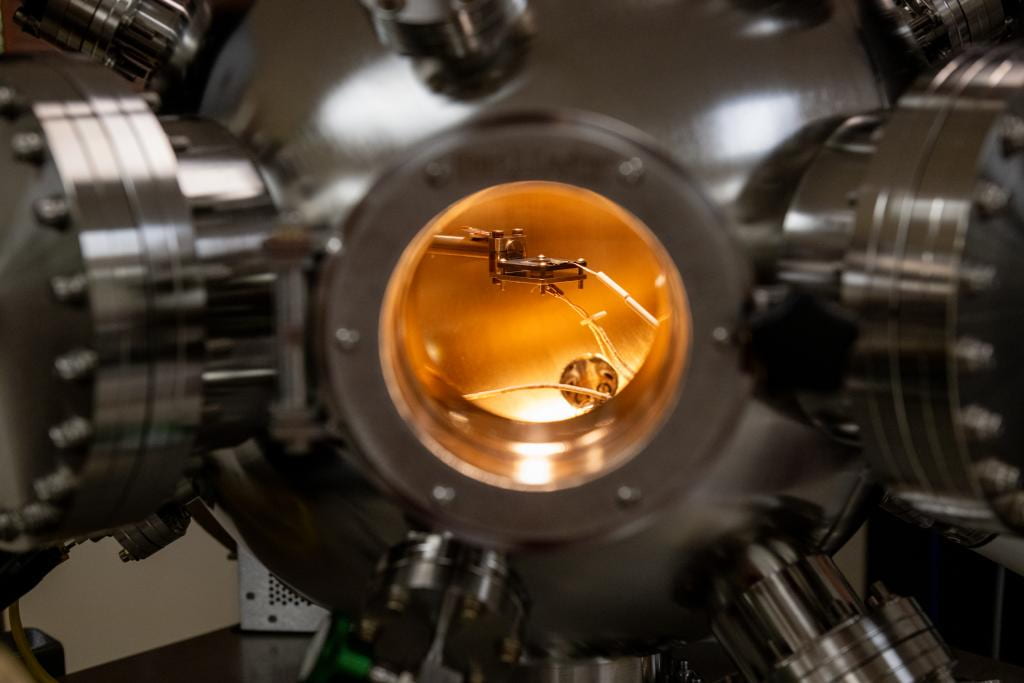
IGNIS II (Ion-Gas-Neutral Interactions with Surfaces) In-situ Surface Science Facility
The IGNIS generation of facilities, IGNIS-1 (located at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign) and IGNIS-2 (located at Penn State University) are state-of-the art in-situ experimental surface science facilities capable of surface characterization of materials under extreme conditions such as those found in nuclear fusion environments or irradiation-driven conditions. The acronym “ignis” means “fire” in latin and encompasses the ability to expose surfaces to a collection of energetic particles under high-pressure and high-temperature environmental conditions during surface analysis measurements. This unique approach allows x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, ion-scattering spectroscopy, and additional surface characterization in a single chamber during the following conditions: High-intensity plasma irradiation using a hollow-cathode plasma source, neutral atom irradiation from a broad beam source with a neutralizer, photon irradiation with a UV source or laser, and electron irradiation using an e-beam source. The charged particle spectroscopy uses a Specs PHOIBOS 150 high-pressure hemispherical analyzer.
IGNIS-2 adds further capability to IGNIS-1 by incorporating a multi chamber manipulator enabling in-vacuo exchange of samples from a fully automated and inert atmosphere glove box to multiple test stands. These include a Liquid Metal dropper system for wettability measurements under vacuum conditions, a reactive system, and T1 which is the primary analysis chamber.
MAPP (Materials Analysis Particle Probe)
MAPP is an in-situ characterization device, designed to be attached to fusion reactors, expose an ensemble of samples and characterized them in a shot to shot basis. MAPP is equipped with a set of diagnostics that allow us to register chemical changes in our samples after their interaction with fusion plasmas. MAPP’s capabilities include X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), Thermal Desorption Spectroscopy (TDS), Ion Scattering Spectroscopy (ISS) and Direct Recoil Spectroscopy (DRS).